Carbon & its Compounds
Importance of Carbon
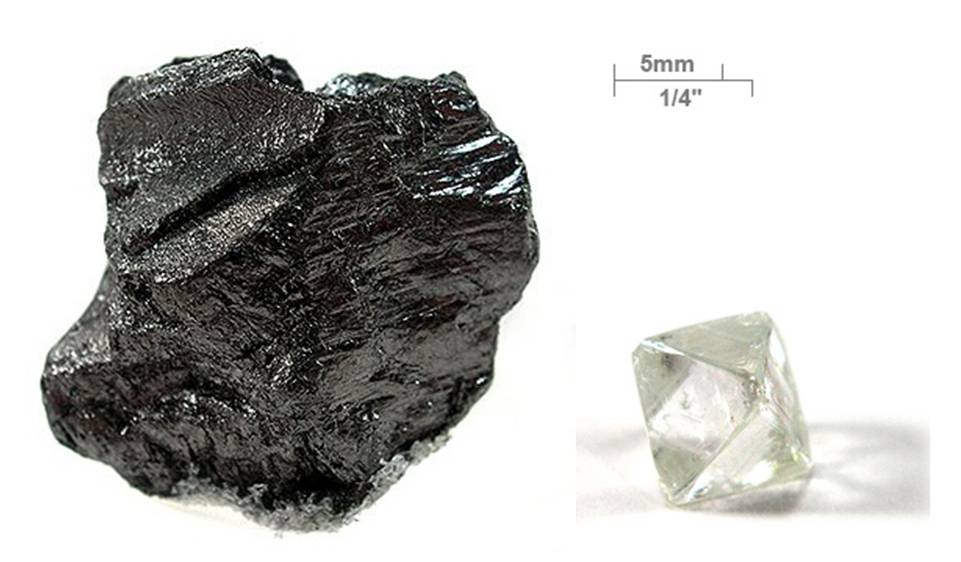


1.All living structures are Carbon based.
2.Earth's Crust has 0.02% Carbon as Carbonates, Hydrocarbons, Coal & Petroleum
3.Atmosphere has 0.03% Carbon as Carbon di-oxide.




 PETROLEUM
PETROLEUM
Physical Properties of Carbon Compounds
1.Poor Conductor of Electricity (Reason: No formation of ions)
2.Low Melting & Boiling points (Reason: Forces of attraction between molecules is not so strong)
What is Reactivity?
The tendency of an atom to attain
1.Completely filled outer shell
2.Noble Gas / Octet Configuration
Either by Gaining / Losing Electrons.
How Carbon forms Compound?
Carbon doesn't form a cation (+4) or an anion(-4) as it becomes unstable.
Reasons
Doesn't form C(+4) as it involves huge amount of energy of ionisation
Doesn't form C(-4) as nucleus will not be able to hold to 4 extra electrons.
Covalent Bonding
Carbon overcomes this problem by covalent bonding through sharing of valence electrons to achieve Octet / Noble Gas Configuration.

Methane


1.Compound of Carbon
2.Widely used as Fuel
3.Major Component of Bio-Gas & CNG (Compressed Natural Gas)
Properties of Covalent Compounds
1.Low Melting & Boiling Points (Reason: Weak Inter-Molecular Forces)
2.Poor Conductors of Electricity (Reason: Sharing of electrons, thus no formation of ions/charges)
Allotrophy
Phenomenon where elements can exist in two or more physical forms.
1.Allotrpes have different structural arrangements of atoms.
2.Physical properties are different
3.Chemical properties are same
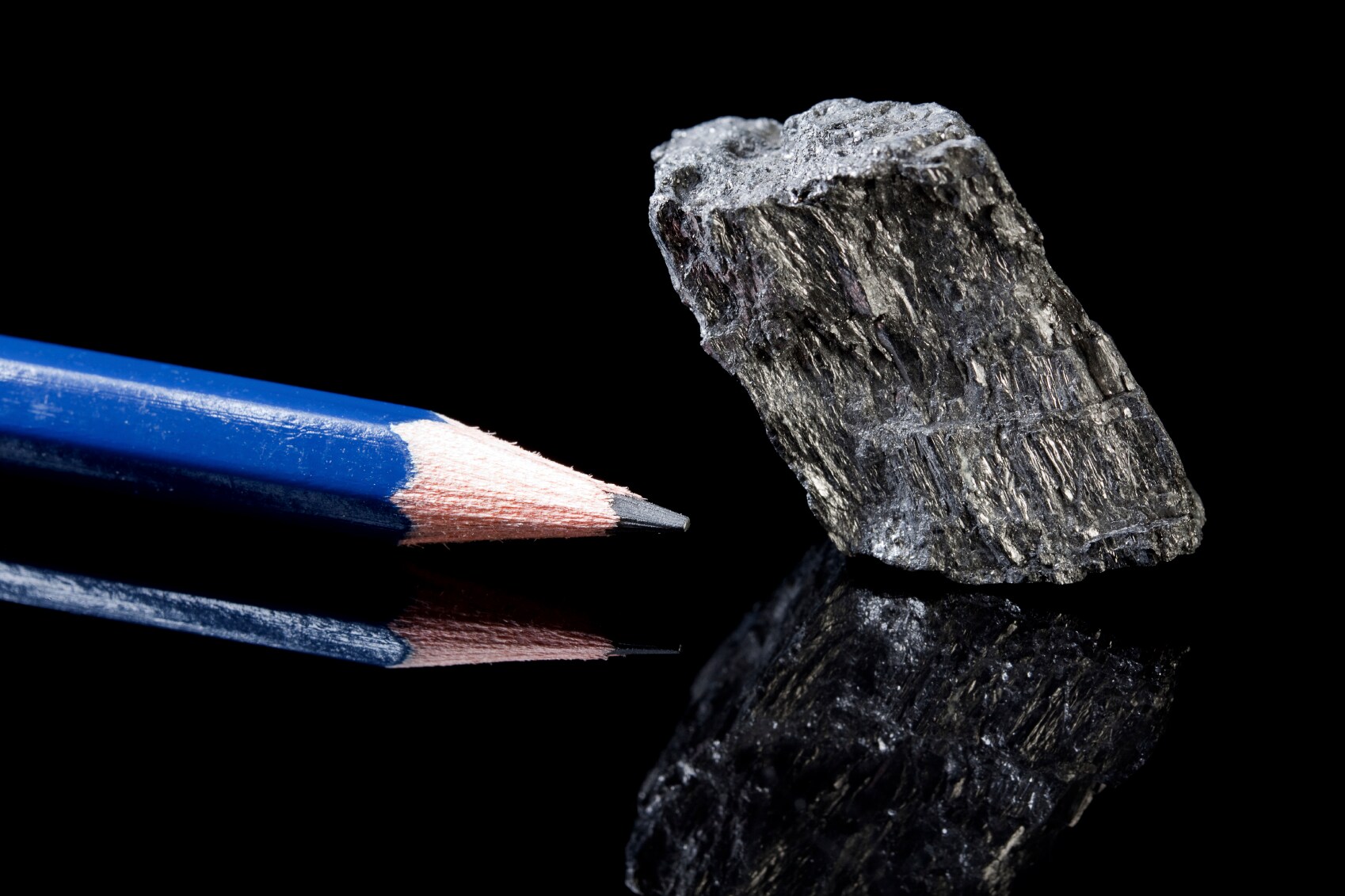
Allotropes of Carbon
DIAMOND - Hardest Substance

GRAPHITE - Good Conductor of Electricity, Slippery Soft

FULLERENES - Buckminsterfullerene C-60 - Foot Ball Shaped

What are Synthetic Diamonds?
Diamonds can be synthesized by subjecting pure carbon to high temperature & pressure.

CVD: Chemical Vapor Deposition
HPHT: High Pressure High Temperature
Catenation
The property through which carbon forms bond with other carbon atoms to form large molecules.
These compounds have
1.Long Chains of Carbon

2.Branched Chains of Carbon
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/isopentane-5a53b55baad52b0036628e8c.png)
3.Ring Arrangement of Carbon

The Carbon atoms get linked by Single / Double / Triple Bonds.
Saturated Carbon Compounds
Compounds of carbon which are linked by Single Bonds.
Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
Compounds of carbon which are linked by Double / Triple Bonds.

Why Carbon-Carbon bond is strong?
Carbon atom size is very small. This enables the nucleus to hold on to the shared pair of electrons strongly. Hence, these compounds are stable.
What is the Valency of Carbon Atom?
Valency = 4. Carbon is a tetravalent atom.
What are Organic Compounds?
Compounds which were initially extracted from natural substances.
Carbon Componds were formed within a living system.
Hence, Carbon compounds except for Carbonates, Hydrocarbonate Salts & Oxides are studied under Organic Chemistry.
Alkanes

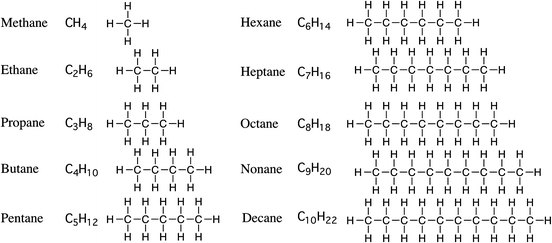
Structural Formulae

Cyclo-Alkanes

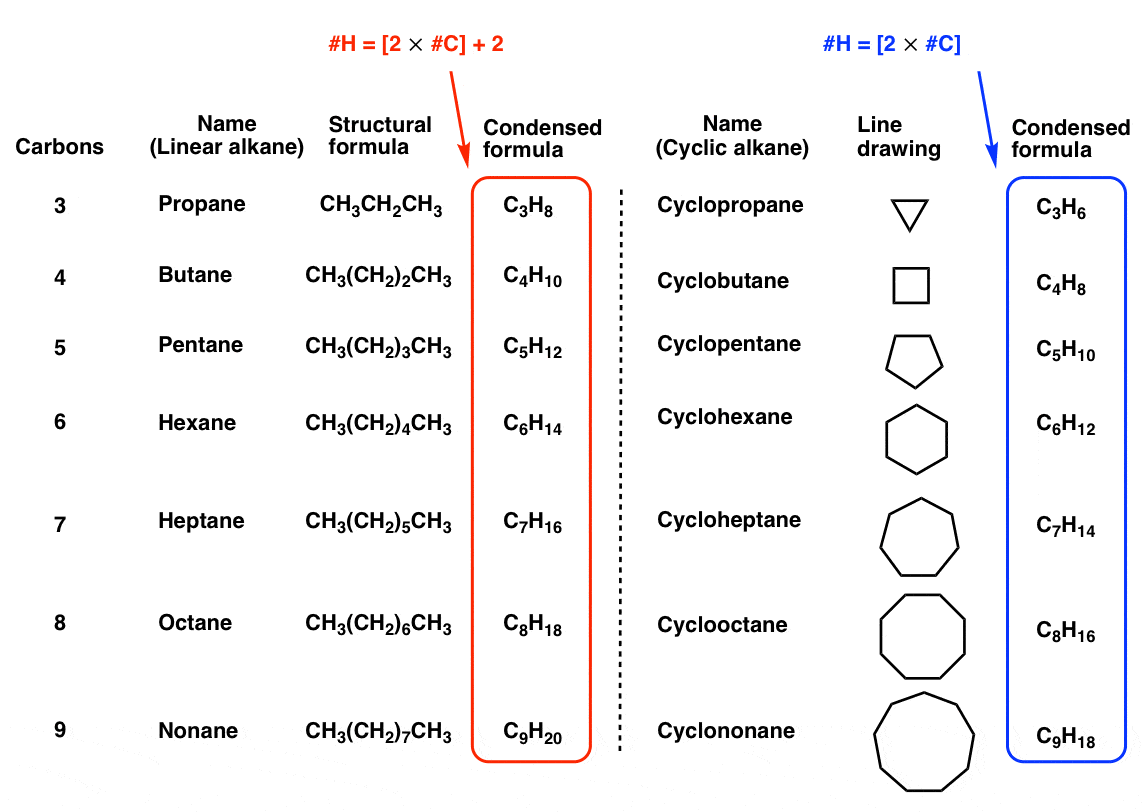
Alkanes Vs Alkenes Vs Alkynes

Hetero-Atom
In a Hydro Carbon Chain one or more hydrogen atoms can be replaced by elements such that valency of carbon is satisfied.
The element replacing hydrogen atoms are known as Hetero-Atoms.
Functional Groups
Functional Groups are Hetero Atoms which gives specific properties to the compounds, regardless the length and nature of the carbon chain. Hence, are called Functional Groups.
Note
a. Free Valencies or group valency is shown by a single line.
b.Functional Group attaches to carbon chain by replacing one H atom through this valency.

Some Additional Functional Groups for Knowledge

Homologous Series
Series of carbon compounds in which the same functional group substitutes the hydrogen atom in a Carbon Chain.

Note
1.Molecular mass increases in a Homologous series
2.There is a gradation of physical properties along the Homologous Series.
3.Melting & Boiling points increase with an increase of Molecular Mass.
4.Chemical properties solely remain on the functional groups.
Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
Naming of Carbon Compounds as per the convention of
IUPAC (International Union for Pure & Applied Chemistry)
Excercise - 1 (Difficult)

Excercise - 2 (Medium)

Excercise - 3

Excercise - 4 (Easy)

Excercise -5 (Very Easy)
Excercise - 6 (Very Very Easy)

Excercise - 7 (Self Excercise)
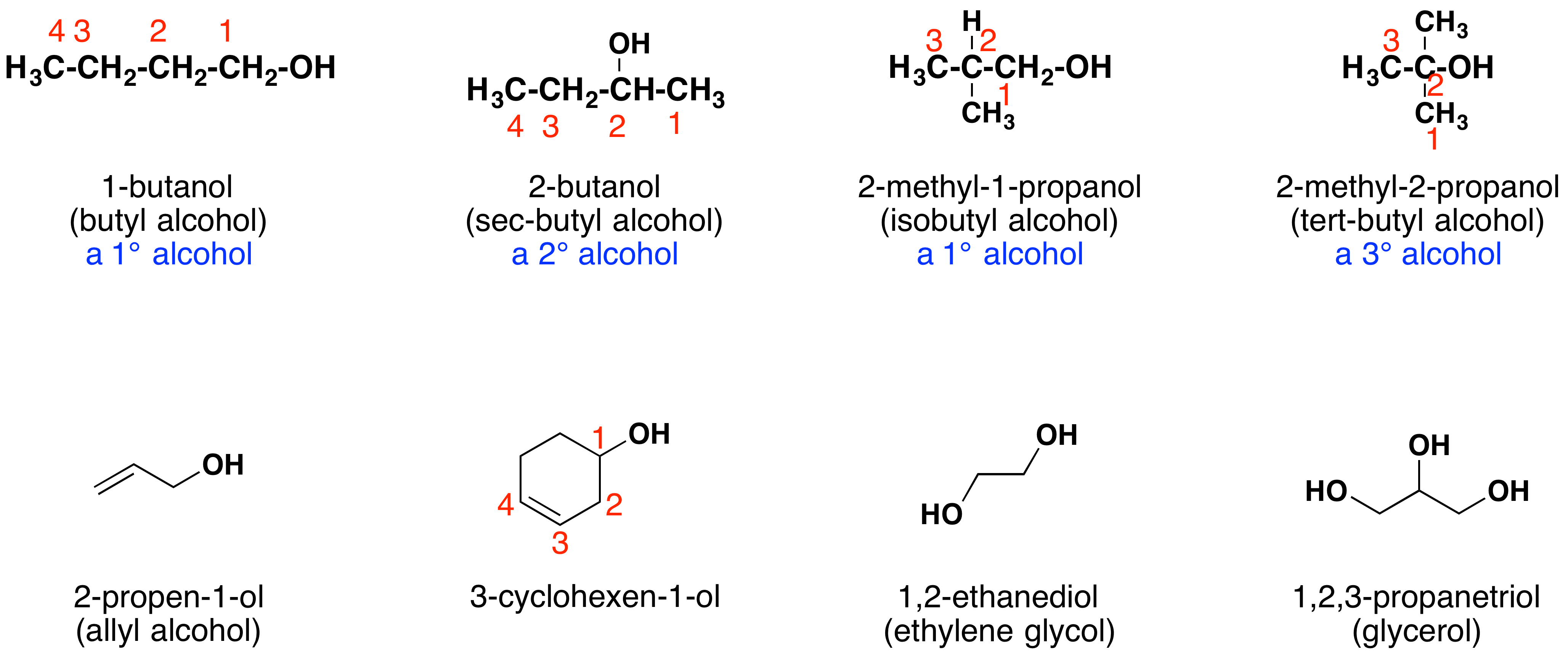
Nomenclature Quiz (10 Marks) (2,3,3,2)



1.All living structures are Carbon based.
2.Earth's Crust has 0.02% Carbon as Carbonates, Hydrocarbons, Coal & Petroleum
3.Atmosphere has 0.03% Carbon as Carbon di-oxide.




 PETROLEUM
PETROLEUMPhysical Properties of Carbon Compounds
1.Poor Conductor of Electricity (Reason: No formation of ions)
2.Low Melting & Boiling points (Reason: Forces of attraction between molecules is not so strong)
What is Reactivity?
The tendency of an atom to attain
1.Completely filled outer shell
2.Noble Gas / Octet Configuration
Either by Gaining / Losing Electrons.
How Carbon forms Compound?
Carbon doesn't form a cation (+4) or an anion(-4) as it becomes unstable.
Reasons
Doesn't form C(+4) as it involves huge amount of energy of ionisation
Doesn't form C(-4) as nucleus will not be able to hold to 4 extra electrons.
Covalent Bonding
Carbon overcomes this problem by covalent bonding through sharing of valence electrons to achieve Octet / Noble Gas Configuration.

Methane


1.Compound of Carbon
2.Widely used as Fuel
3.Major Component of Bio-Gas & CNG (Compressed Natural Gas)
Properties of Covalent Compounds
1.Low Melting & Boiling Points (Reason: Weak Inter-Molecular Forces)
2.Poor Conductors of Electricity (Reason: Sharing of electrons, thus no formation of ions/charges)
Allotrophy
Phenomenon where elements can exist in two or more physical forms.
1.Allotrpes have different structural arrangements of atoms.
2.Physical properties are different
3.Chemical properties are same
Allotropes of Carbon
DIAMOND - Hardest Substance
GRAPHITE - Good Conductor of Electricity, Slippery Soft

FULLERENES - Buckminsterfullerene C-60 - Foot Ball Shaped

What are Synthetic Diamonds?
Diamonds can be synthesized by subjecting pure carbon to high temperature & pressure.

CVD: Chemical Vapor Deposition
HPHT: High Pressure High Temperature
Catenation
The property through which carbon forms bond with other carbon atoms to form large molecules.
These compounds have
1.Long Chains of Carbon

2.Branched Chains of Carbon
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/isopentane-5a53b55baad52b0036628e8c.png)
3.Ring Arrangement of Carbon
The Carbon atoms get linked by Single / Double / Triple Bonds.
Saturated Carbon Compounds
Compounds of carbon which are linked by Single Bonds.
Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
Compounds of carbon which are linked by Double / Triple Bonds.
Why Carbon-Carbon bond is strong?
Carbon atom size is very small. This enables the nucleus to hold on to the shared pair of electrons strongly. Hence, these compounds are stable.
What is the Valency of Carbon Atom?
Valency = 4. Carbon is a tetravalent atom.
What are Organic Compounds?
Compounds which were initially extracted from natural substances.
Carbon Componds were formed within a living system.
Hence, Carbon compounds except for Carbonates, Hydrocarbonate Salts & Oxides are studied under Organic Chemistry.
Alkanes


Structural Formulae

Cyclo-Alkanes


Alkanes Vs Alkenes Vs Alkynes
Hetero-Atom
In a Hydro Carbon Chain one or more hydrogen atoms can be replaced by elements such that valency of carbon is satisfied.
The element replacing hydrogen atoms are known as Hetero-Atoms.
Functional Groups
Functional Groups are Hetero Atoms which gives specific properties to the compounds, regardless the length and nature of the carbon chain. Hence, are called Functional Groups.
Note
a. Free Valencies or group valency is shown by a single line.
b.Functional Group attaches to carbon chain by replacing one H atom through this valency.

Some Additional Functional Groups for Knowledge

Homologous Series
Series of carbon compounds in which the same functional group substitutes the hydrogen atom in a Carbon Chain.

Note
1.Molecular mass increases in a Homologous series
2.There is a gradation of physical properties along the Homologous Series.
3.Melting & Boiling points increase with an increase of Molecular Mass.
4.Chemical properties solely remain on the functional groups.
Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
Naming of Carbon Compounds as per the convention of
IUPAC (International Union for Pure & Applied Chemistry)
Excercise - 1 (Difficult)
Excercise - 2 (Medium)
Excercise - 3

Excercise - 4 (Easy)
Excercise -5 (Very Easy)
Excercise - 6 (Very Very Easy)
Excercise - 7 (Self Excercise)

Nomenclature Quiz (10 Marks) (2,3,3,2)



Comments
Post a Comment